System Design-2
In the previous article, I have explained about databases and it’s importance in System Design. Now we will talk about properties of distributed system and CAP theorem (Brewer’s theorem).
Properties of distributed system
There is three main properties of distributed system.
Consistency
Availability
Partition Tolerance
Consistency :- The name explain itself that distributed system should always be consistent. It means all the nodes should have same data at anytime. If any write operation execute then it will update all the nodes then system will show a successful message otherwise it will roll back if any error occur.
Availability :- System should always be available even if there is high load. It means every request should get a response even if one or more than one nodes are down.
Partition Tolerance :- System should continue to work despite message loss or partial failure (partition (communication break) between nodes). It means system should handle any amount of failure that does not result in entire network failure.
CAP Theorem (Brewer’s Theorem) :- It says that any distributed system can not achieve all these three properties. Only 2 of them can be achieved on expense of other.
Therefore, while designing distributed system, choose database carefully according to your requirements.
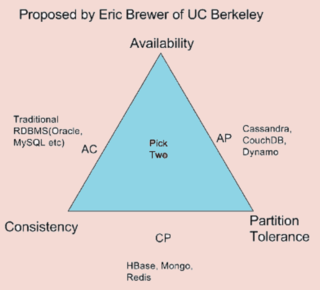
Databases are classified based on CAP characteristics they support :-
CP databases :- A CP database focus on consistency and partition tolerance. When a partition (communication break) occurs between any two nodes, the system has to shut down the non-consistence node until the partition in resolved.
AP database :- An AP database delivers availability and partition tolerance. when partition occurs, all nodes remains available but those those nodes that is wrong end of partition might return an older version of data than others.
CA databases :- A CA database delivers consistency and availability across all nodes. It can not do this if there is a partition between any two nodes in the system.
Note :- in a distributed system, partitions can’t be avoided. So, while we can discuss a CA distributed database in theory, for all practical purposes a CA distributed database can’t exist. This doesn’t mean you can’t have a CA database for your distributed application if you need one. Many relational databases, such as PostgreSQL, deliver consistency and availability and can be deployed to multiple nodes using replication.
As we are talking about distributed system, therefore splitting up database is an important task. This splitting up the database across multiple machines to improve the scalability is known as Sharding a*nd all the splitted databases is known as **Shards**. sharding is the process of horizontal scaling, which improves manageability, performance, availability and load balancing.*
Sharding techniques:-
Horizontal partitioning
Vertical partitioning
Directory based partitioning
Hash-based partitioning
That’s all for this article. In the next article I will explain each sharding techniques in detail and problem of sharding.